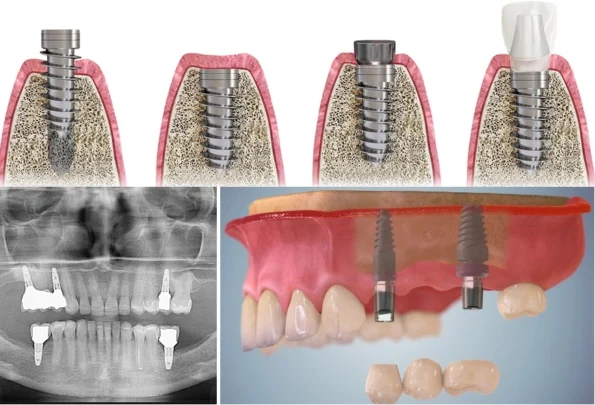
Navigating Dental Implant Complications
By proactively addressing and effectively managing these potential complications, dental professionals can ensure the long-term success and stability of dental implant treatment for their patients.
Regular monitoring, patient education, and collaboration between the dental team and specialists are essential components of navigating dental implant complications successfully.
1. Infection Management:
- Infections at the implant site can lead to implant failure if left untreated.
- Proper management involves prescribing antibiotics to eliminate bacterial infection, along with thorough cleaning of the implant site to remove any debris or plaque buildup.
- In severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to address deep-seated infections.
2. Implant Stability Assessment:
- Monitoring implant stability is crucial during the healing phase following implant placement.
- Any signs of implant mobility or loosening should be promptly addressed to prevent further complications.
- Techniques such as resonance frequency analysis (RFA) and periapical radiographs can aid in assessing implant stability and detecting early signs of complications.
3. Soft Tissue Management:
- Maintaining healthy soft tissues surrounding the implant is essential for long-term implant success.
- Regular professional cleanings, along with proper oral hygiene practices at home, help prevent inflammation and peri-implantitis.
- Additionally, techniques such as guided tissue regeneration (GTR) may be employed to regenerate lost soft tissue and improve the health of the peri-implant mucosa.
4. Bone Loss Prevention:
- Peri-implant bone loss can compromise the stability of dental implants and increase the risk of implant failure.
- Strategies for preventing bone loss include meticulous surgical technique, appropriate implant selection and placement, and the use of bone grafts or augmentation procedures when necessary.
- Regular follow-up visits allow for early detection of bone loss and prompt intervention to preserve implant stability.
5. Nerve Damage Management:
- Nerve damage during implant placement can result in sensory disturbances such as numbness or tingling in the lips, tongue, or chin.
- Careful surgical planning and technique can help minimize the risk of nerve injury.
- In cases where nerve damage occurs, conservative management and close monitoring of sensory function are essential.
- Referral to a specialist may be warranted for further evaluation and management of nerve injuries.
6. Sinus Complication Resolution:
- Dental implants placed in the posterior maxilla may inadvertently penetrate the maxillary sinus, leading to sinus complications such as sinusitis or sinus infections.
- Proper diagnosis and management of sinus complications involve collaboration between dental and medical professionals.
- Techniques such as sinus lift procedures and sinus augmentation may be employed to address compromised sinus integrity and restore implant stability.